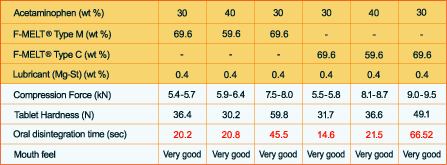
1. Sample formulations:Acetaminophen formulation with F-MELT® Type C and M
A 30-40% load of acetaminophen may bring down the tablet hardness to a region between 30 and 35 N while maintaining a disintegration time of 30 seconds. At higher compression forces, the oral disintegration time tends to increase slightly.
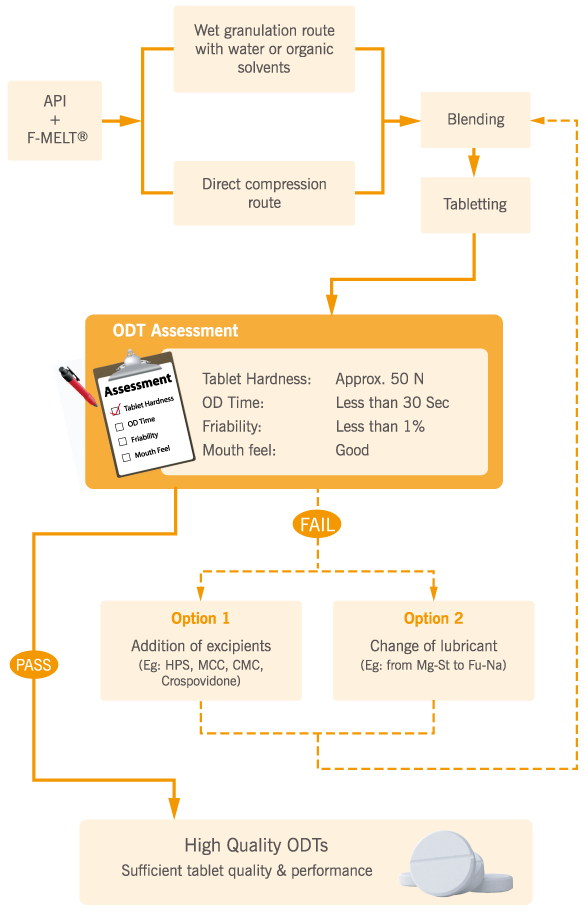
A strategy to overcome this limitation was developed by Fuji scientists to maintain tablet hardness of 50 N and an oral disintegration time of 30 seconds.
Strategy for preparing high quality F-MELT® tablets
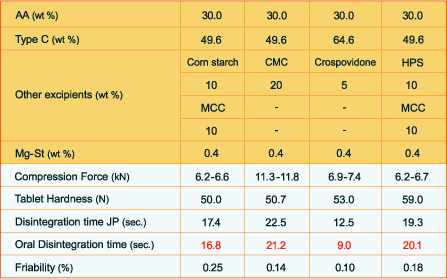
HPS-Hydroxypropyl Starch,MCC - Microcrystalline Cellulose,
CMC - Carboxymethyl Cellulose, Mg.St – Magnesium Stearate,
Fu-Na: Sodium Stearyl Fumarate.
Two approaches to obtain optimum tablet hardness, an oral disintegration time of less than 30 seconds and a pleasant mouth feel are:
a. By incorporating additional excipients like microcrystalline cellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose, starches etc in amounts less than 20%)
b. By choosing a more hydrophilic lubricant such as sodium stearyl fumarate.
2. F-MELT® Sample Formulations with Acetaminophen (AA) and additional pharmaceutical excipients, focusing on higher tablet hardness and shorter oral disintegration time
Example 1. Acetaminophen formulations with additional excipients like corn starch, carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), crospovidone and hydroxypropyl starch (HPS) and Magnesium stearate as lubricant.
The F-MELT® acetaminophen tablets achieve a tablet hardness of 50 N, a disintegration time of less than 30 seconds with low friability
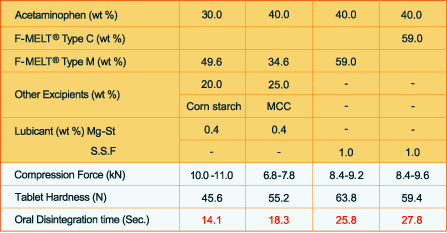
Example 2. F-MELT® acetaminophen formulations with additional excipients like corn starch, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and change of lubricant.
Tabletting conditions: Φ8 mm, 200 mg/tablet rotary:15rpm; MCC: Microcrystalline cellulose
Mg-St: Magnesium stearate; S.S.F Sodium Stearyl Fumarate
By changing the lubricant, formulators could avoid adding additional excipients to achieve a higher tablet hardness and a disintegration time of less than 30 seconds.
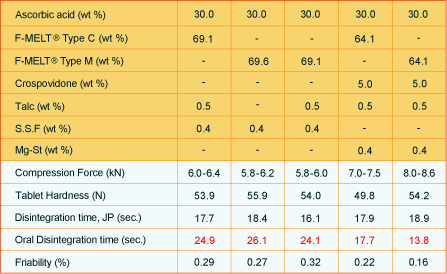
3. F-MELT® sample formulation with L-Ascorbic acid. Effect of two different types of lubricants (sodium stearyl fumarate and magnesium stearate) on tablet hardness, oral disintegration time and friability
Tabletting conditions: Φ8 mm, 200 mg/tablet rotary:15rpm.
Mg-St: Magnesium stearate; S.S.F Sodium Stearyl Fumarate
Ascorbic acid, a highly hygroscopic active was successfully formulated into an oral disintegrating tablet with F-MELT®. In order to avoid the sticking/capping, 0.5% of talc was included in the formulation